By default, if you do not create any access control policies after enabling the Internet firewall, Cloud Firewall allows all traffic. You can create outbound and inbound access control policies for the Internet firewall to prevent unauthorized access between Internet-facing assets and the Internet. This topic describes how to create inbound and outbound access control policies for the Internet firewall.
Prerequisites
The Internet firewall is enabled for your Internet-facing assets. For more information about how to enable the Internet firewall, see Enable the Internet firewall.
For more information about the Internet-facing assets that can be protected by Cloud Firewall, see Protection scope.
Ensure that you have a sufficient quota for access control policies. You can view the quota usage on the page. For more information about how to calculate quota usage, see Overview of access control policies.
If the remaining quota is insufficient, you can click Increase Quota to increase the value of Quota for Additional Policy. For more information, see Purchase Cloud Firewall.

If you want to add multiple objects as an access source or destination, make sure that an address book that contains the objects is created. For more information, see Manage address books.
Create access control policies for the Internet firewall
Cloud Firewall allows you to create custom policies and provides recommended policies that you can apply.
Create custom policies: You can create custom policies based on your business requirements.
Apply recommended intelligent policies: Cloud Firewall automatically learns your traffic within the previous 30 days and recommends multiple intelligent policies based on the traffic risks that are identified. You can determine whether to apply the policies.
Apply recommended common policies: Cloud Firewall recommends common policies. If the recommended common policies meet your business requirements, you can apply the policies.
We recommend that you allow access to the open ports on which services are provided for an open public IP address on the Internet firewall and deny access to other ports. This reduces the exposure of your assets to the Internet.
If you want to allow access from trusted sources such as IP addresses or domain names and deny access to other sources, we recommend that you first create a policy that allows access from the trusted sources and has a higher priority and then create a policy that denies traffic from all sources and has a lower priority.
If you do not apply recommended intelligent policies or recommended common policies, the policies do not take effect.
Create a custom policy
You can create a custom outbound or inbound policy for the Internet firewall based on your business requirements.
Log on to the Cloud Firewall console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Outbound or Inbound tab, select IPV4 or IPV6 from the drop-down list and click Create Policy. By default, an access control policy for IPv4 addresses is created.

In the Create Outbound Policy or Create Inbound Policy panel, click the Create Policy tab.
Configure the policy based on the following table and click OK.
Apply recommended intelligent policies
Cloud Firewall automatically learns your traffic from the previous 30 days and recommends multiple intelligent policies based on the traffic risks that are identified. If the recommended intelligent policies meet your business requirements, you can apply the policies.
You can apply both outbound and inbound intelligent policies that are recommended.
Before you apply a recommended policy, make sure that you understand its meaning and the possible impacts on services.
You can ignore recommended intelligent policies. After you ignore a recommended intelligent policy, the policy cannot be restored. Proceed with caution.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Go to the Recommended Intelligent Policy page. You can use one of the following methods:
In the upper-right corner above the policy list, click Intelligent Policy. In the panel that appears, click the Outbound or Inbound tab.

On the Outbound or Inbound tab, click Create Policy. In the panel that appears, click the Recommended Intelligent Policy tab.
View and apply the recommended intelligent policies. You can find a policy and click Apply Policy. Alternatively, you can select multiple policies and click Batch Dispatch.
Apply recommended common policies
If the recommended common policies meet your business requirements, you can apply the policies.
Before you apply a recommended policy, make sure that you understand its meaning and the possible impacts on services.
You can ignore recommended common policies. After you ignore a recommended common policy, the policy cannot be restored. Proceed with caution. If you ignore all recommended common policies, the Recommended Common Policy tab is no longer displayed.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Outbound or Inbound tab, click Create Policy. In the panel that appears, click the Recommended Common Policy tab.
View and apply the recommended common policies. You can find a policy and click Quick Apply.
Configure the access control engine mode
The access control engine supports the Loose Mode and Strict Mode.
Loose Mode (default): After you enable the loose mode, traffic whose application type or domain name is identified as Unknown is allowed. This ensures normal access.
Strict Mode: After you enable the strict mode, the traffic whose application type or domain name is identified as Unknown is matched against all policies you configured. If you configured a Deny policy, this type of traffic is denied.
Cloud Firewall allows you to configure the default access control engine mode for new assets, change the access control engine mode for a single asset, and change the access control engine mode for multiple assets at the same time. To perform the preceding operations, go to the page. On the Internet Border page, click ACL Engine Mode in the upper-right corner of the access control policy list. Then, perform the required operations in the Access Control Engine Management - Internet Border panel.


Configure the default access control engine mode for new assets
Change the access control engine mode for an asset
Change the access control engine mode for multiple assets at the same time
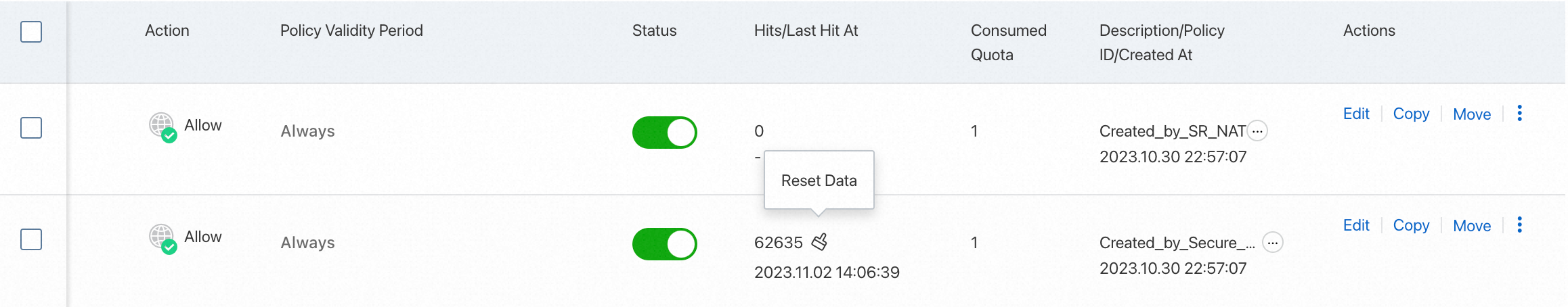
View policy hits
After your business runs for a period of time, you can view the hit count and last hit time of access control policies in the HitsLast Hit At column of the access control policy list.
You can click the hit count to go to the Traffic Logs page to view traffic logs. For more information about how to view traffic logs, see Log Audit.
What to do next
After you create a custom policy, you can find the policy in the list of custom policies and click Edit, Delete, or Copy in the Actions column to manage the policy. You can download the list of custom policies, delete multiple policies at a time, and click Move to change the priority of the policy.
A valid priority value ranges from 1 to the number of existing policies. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. After you change the priority of a policy, the priorities of policies that have lower priorities decrease.
After you delete a policy, Cloud Firewall no longer manages traffic on which the policy is originally in effect. Proceed with caution.
References
For more information about how to manage traffic from Internet-facing assets to a specified domain name, see Configure a policy to allow only Internet-facing servers to access a specified domain name.
For more information about how to perform access control on a specified region, see Configure a policy to deny traffic destined for a server from regions outside China.
For more information about how access control policies work, see Overview of access control policies.
For more information, see Configure access control policies.
For more information about how to view and manage IP address books, port address books, and domain address books in access control policies, see Manage address books.
For more information about how to configure and use access control policies, see FAQ about access control policies.





