If the default kubelet configuration does not meet your needs, you can customize kubelet parameters for a node pool to adjust node behavior. For example, you can adjust resource reservations to manage resource usage, customize node-pressure eviction thresholds to mitigate resource shortages, or change the topology manager policy to improve system performance.
Limits
Only ACK clusters that run version 1.20 or later support custom kubelet parameters. To upgrade your cluster, see Manually upgrade an ACK cluster.
Only ACK Lingjun clusters that run version 1.22 or later support custom kubelet parameters. To upgrade your cluster, see Upgrade a cluster.
If your cluster version does not meet these conditions, unexpected behavior may occur.
Precautions
Custom kubelet parameters change node configurations in batches. The changes take effect immediately on existing nodes in the node pool. New nodes also use the new configuration. When the changes take effect, the kubelet process restarts. This may affect running nodes and workloads. We recommend that you perform this operation during off-peak hours.
If `evictionHard`, `kubeReserved`, or `systemReserved` is not configured, the system uses default values for resource reservation. For more information about how the default values are calculated, see Node resource reservation policy.
Changes to the resource reservation configuration may reduce a node's allocatable resources. For nodes with high resource usage, this may trigger node eviction.
Do not use the command line to define kubelet parameters that are not supported in the console. This operation poses significant stability risks. You are responsible for ensuring the correctness and compatibility of the user data file. Incorrect configurations or configurations that are deprecated in new versions can cause nodes to become unavailable.
When the kubelet starts, it merges configurations from different sources based on their priority. If the same configuration item is set in multiple ways, the setting with the higher priority overwrites the setting with the lower priority.
Customize kubelet parameters for a node pool in the console
When custom kubelet parameters are applied, the kubelet process restarts. This may affect your services. We recommend that you perform this operation during off-peak hours.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Node Pools page, click
 > Kubelet Configuration in the Actions column of the target node pool.
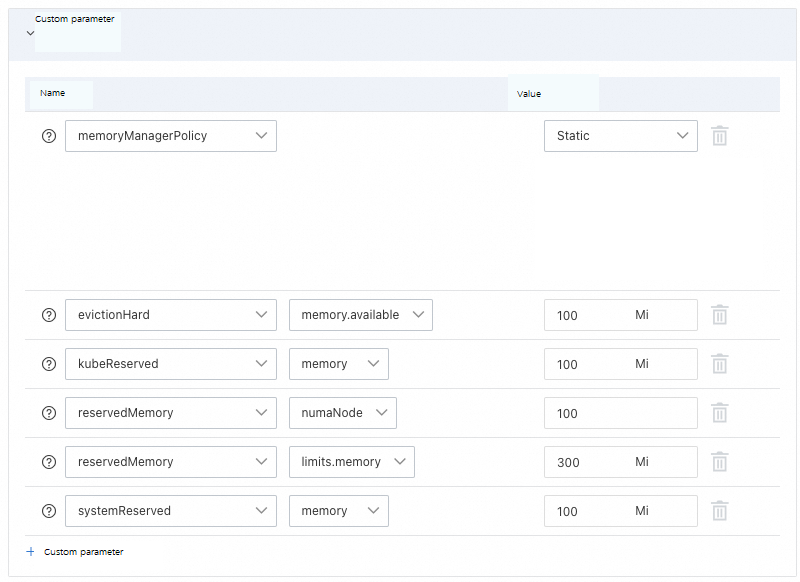
> Kubelet Configuration in the Actions column of the target node pool.Read the precautions on the page. Click Custom Parameters, select the parameters to configure, specify the nodes to upgrade, and configure a batch update policy. Then, click Submit and follow the on-screen instructions.
The batch update policy is described as follows:
Maximum Concurrent Nodes Per Batch: Kubelet configurations are applied to nodes in batches. This process takes some time. You can view the progress and control the process, such as pause, resume, or cancel, in the event list.
Interval Between Batches: The time interval between batches.
You can use the pause feature to verify the upgraded nodes. When you pause the task, the configuration of the current nodes is completed. Nodes that have not yet started are not configured until you resume the task.
We recommend that you complete the custom configuration task in a timely manner. A paused task is automatically canceled after seven days. The related events and logs are also cleared.
In addition to using the console, you can also call the ModifyNodePoolNodeConfig operation to customize kubelet parameters. The following section describes the customizable kubelet parameters that are supported by ACK.
Customizable kubelet parameters
Field | Description | Default value | Recommended value range |
allowedUnsafeSysctls | Specifies the unsafe sysctls or sysctl wildcard characters (patterns that end with Important Before using this parameter, carefully assess the risks and ensure availability. | N/A | Supports sysctl configurations with the following prefixes:
|
containerLogMaxFiles | The maximum number of log files for a container. The value must be 2 or greater. The container runtime must be containerd. | 10 | [2, 10]. |
containerLogMaxSize | The maximum size of a container log file before it is rotated. The container runtime must be containerd. | 100Mi | N/A. |
cpuCFSQuota | Enables CPU CFS quota enforcement for containers with CPU limits. | true | Valid values:
|
cpuCFSQuotaPeriod | Sets the CPU CFS quota period. The CustomCPUCFSQuotaPeriod feature gate must be enabled. | 100ms | A value from 1 millisecond to 1 second, inclusive. |
cpuManagerPolicy | The CPU manager policy. | none | Valid values:
|
eventBurst | The maximum burst for event creation. | 10 | [1, 100]. The value must be greater than or equal to the value of |
eventRecordQPS | The number of events that can be generated per second. | 5 | [1, 50]. |
evictionHard | A set of hard eviction thresholds that trigger pod eviction. | imagefs.available<15%,memory.available<300Mi,nodefs.available<10%,nodefs.inodesFree<5% | None. |
evictionSoft | A set of soft eviction thresholds. | None | None. |
evictionSoftGracePeriod | A set of eviction grace periods. Note `evictionSoft` must be set. | None | None. |
featureGates | A set of key-value pairs that describe feature gates for experimental features. Each gate is represented as
Important
| N/A | N/A. |
imageGCHighThresholdPercent | The percentage of disk usage that triggers image garbage collection. Image garbage collection runs when disk usage exceeds this threshold. This value must be greater than the value of `imageGCLowThresholdPercent`. | 85 | [60, 95]. |
imageGCLowThresholdPercent | The percentage of disk usage at which image garbage collection does not run. Image garbage collection does not run if disk usage is below this threshold. This value must be less than the value of `imageGCHighThresholdPercent`. | 80 | [30, 90]. |
kubeAPIBurst | The maximum number of burst requests sent to the API server per second. | 10 | [1, 100]. The value must be greater than or equal to the value of |
kubeAPIQPS | The number of queries per second (QPS) to the API server. | 5 | [1, 50]. |
kubeReserved | The resource configuration reserved for the Kubernetes system. | The value is automatically calculated by default. For more information, see Node resource reservation policy. | N/A. |
maxPods | The maximum number of pods that can run on a node. Important Modifying the value of `maxPods` does not affect the number of IP addresses that can be allocated on the node. If the value of `maxPods` is too large, pods that do not use the HostNetwork mode may fail to be assigned an IP address and fail to start. | N/A. The value depends on physical resource configurations such as machine specifications and container network planning. | N/A. |
memoryManagerPolicy | The policy for the memory manager. | None | Valid values:
|
podPidsLimit | The maximum number of process IDs (PIDs) that can be used in each pod. | 16384 | None. |
readOnlyPort | The read-only port for the kubelet that does not require authentication. |
| 0 For information about the risks of opening the read-only port (10255) for kubelet container monitoring, see [Product Change] Migrate the monitoring port of earlier-version ACK clusters to an authenticated port. |
registryBurst | The maximum number of burst image pulls. | 10 | [1, 100]. The value must be greater than or equal to the value of |
registryPullQPS | The maximum QPS for the image repository. | 5 | [1, 50]. |
reservedMemory | A list of memory reservations for NUMA nodes. | None. | None. |
serializeImagePulls | Pulls images serially. | False | Valid values:
|
systemReserved | The resource configuration reserved for the system. | The value is automatically calculated by default. For more information, see Node resource reservation policy. | N/A. |
topologyManagerPolicy | The topology manager policy. With a NUMA architecture, data can be allocated to the same NUMA node to reduce cross-node access and improve system performance. The topology manager can make resource allocation decisions that align with the topology. For more information, see Control Topology Management Policies on a node. | none |
|
containerLogMonitorInterval | The cluster version must be 1.30 or later. The interval at which container logs are checked for rotation. | 10s | [3s,60s] |
containerLogMaxWorkers | The cluster version must be 1.30 or later. The maximum number of concurrent workers for log rotation. | 1 | [1,20] |
tracing | Enables Tracing Analysis for control plane or data plane components of the cluster. For more information, see Manage Tracing Analysis. | None |
|
FAQ
Will custom configurations be deprecated?
As Kubernetes evolves, some parameters or feature gates may be deprecated or removed. If a custom parameter managed by ACK is not applicable to a new version, the related configuration is removed during a cluster upgrade.
How do I use a configuration file to manage the kubelet?
Container Service for Kubernetes adjusts how kubelet configurations are managed based on community best practices. For clusters that run version 1.20 or later, deprecated kubelet command-line flags are gradually replaced by a configuration file. For more information, see Kubelet Configuration (v1beta1).
New nodes, such as newly created nodes and auto-scaled nodes, use both the configuration file and the original configuration method. Existing nodes are not affected. To manage the configurations of all nodes in a node pool using only the configuration file, you can apply a custom configuration as described in Customizable kubelet parameters.
How do I modify a kubelet parameter that is not on the supported list?
ACK lets you write custom parameters to the `/etc/kubernetes/kubelet-customized-args.conf` file. This file stores custom startup parameters and configuration options for the kubelet. Parameters written to this file take precedence over and overwrite values that are set using the custom kubelet configuration feature for node pools when the node restarts.
Adjusting kubelet parameters can cause issues such as node registration failures or pod scheduling failures, and affect your services. Before you proceed, we recommend that you fully assess the risks of the change.
(Recommended) For nodes that will be created in the node pool, you can configure a script in the User Data section of the node pool to write to the custom parameter configuration file. This ensures that new nodes use these custom parameter values by default.
In the User Data section of the node pool configuration, add the following script. Replace
${kubelet_key}and${kubelet_value}with the actual values.Only scripts that use
> /etc/kubernetes/kubelet-customized-args.confor> kubelet-customized-args.confare supported in the User Data section. If you use other methods to modify `kubelet-customized-args.conf` in the Pre-customized User Data section, the `/etc/kubernetes/kubelet-customized-args.conf` file is overwritten during ACK initialization.mkdir -p /etc/kubernetes echo 'KUBELET_CUSTOMIZED_ARGS="--${kubelet_key}=${kubelet_value}"' > /etc/kubernetes/kubelet-customized-args.conf systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart kubeletFor more information about how to access the configuration page, see Create and manage a node pool.
For existing nodes in the node pool, log on to the node to modify the custom parameter configuration file. Then, run the following commands to apply the configuration.
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart kubelet
References
For more information about the configuration items for a node pool, see Create and manage a node pool.
If you encounter errors or abnormal behavior on your nodes, pods, or kubelet, see Troubleshoot abnormal nodes, Troubleshoot abnormal pods, and FAQ about nodes and node pools to troubleshoot the issues.

 For more information, see
For more information, see