spot instances are a type of on-demand instances that cost less than pay-as-you-go instances. You can specify a ratio of spot instances to pay-as-you-go instances in a node pool to reduce resource costs. This topic describes spot instance-based node pools, their use scenarios, how to configure instance types, how to specify instance ratios, how to check instance expiration status, and how spot instances are gracefully shut down.
Introduction
spot instances use the pay-as-you-go billing method. You pay for these instances after you use them, with bills calculated based on market price and billing duration. A spot instance-based node pool consists of both spot instances and pay-as-you-go instances, with a ratio you specify.
spot instances are pay-as-you-go instances whose prices fluctuate dynamically based on factors such as resource availability. Their price can be up to 90% lower than regular pay-as-you-go instances. The market price fluctuates based on changes in supply and demand for the instance type. When creating a spot instance, you must select a bidding mode to bid for a specified instance type. If your bid price exceeds the market price and sufficient stock is available, a spot instance is created.
After creation, you can use a spot instance just like a regular pay-as-you-go instance. You can also use it with other cloud resources such as cloud disks and public IP addresses. The default protection period is 1 hour. After this period ends, the system checks the spot price and resource stock every 5 minutes. If the spot price exceeds your bid price or if stock becomes insufficient, the spot instance is released.
Scenarios
Spot Instance-based Node Pools
spot instances may be unexpectedly reclaimed, making these node pools suitable for stateless applications with high fault tolerance. You can use them for workloads that involve batch processing, machine learning training jobs, queued transaction processing applications, applications that use the REST API, and extract, transform, load (ETL) workloads of big data computing, such as Apache Spark jobs.
You must ensure that workloads deployed in spot instance-based node pools can tolerate node resource unavailability. If they cannot, we recommend deploying them in node pools with pay-as-you-go or subscription instances instead. Workloads that are not tolerant to node resource unavailability include the following:
Cluster management tools, such as monitoring tools and O&M tools.
Stateful workloads or applications, such as database services.
Spot Instance-based Node Pools With Auto Scaling
If your workloads process user traffic that fluctuates in a specific pattern, we recommend enabling auto scaling for the spot instance-based node pool.
With auto scaling enabled, the system automatically checks whether the node pool needs to scale out to host more pods and scales in when the threshold is reached. Node pools with auto scaling can scale out faster than those without it, and idle resources are released more promptly. Faster scale-out ensures sufficient node resources when spot instances are reclaimed, while automatic release of idle resources helps reduce costs.
Select instance types for spot instances
We recommend selecting instance types based on your business requirements while balancing resource availability, cost, and performance. Elastic Compute Service (ECS) provides various instance types to meet different workload requirements. When using a spot instance-based node pool, select a combination of instance types that minimize impact on your workloads when instances are reclaimed.
You can use one of the following methods to select instance types.
Use the console recommendations
Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) console provides suggestions on instance types. When creating or modifying a node pool, available instance types for your selected region are displayed. After selecting instance types, the console automatically provides recommendations, displays the scalability of the node pool, and shows the price range of each spot instance. You can adjust your selections and specify price limits based on this information.
For more information about how to create or modify a node pool, see Create and manage node pools.

Use the spot-instance-advisor command-line tool
ACK provides an open source command-line tool spot-instance-advisor that you can use to query the historical and current prices of spot instances. spot-instance-advisor calls API operations to retrieve the historical prices of instance types in a region. It calculates the hourly vCPU unit price based on the obtained statistics and lists the instance types with the lowest hourly vCPU unit prices. The tool also calculates the entropy of the hourly vCPU unit price for each instance type. A higher entropy value indicates more frequent price fluctuations. We recommend that you select instance types whose hourly vCPU unit prices have a low entropy value.
Download spot-instance-advisor. For more information, see spot-instance-advisor.
spot-instance-advisor supports the following parameters.
Usage of ./spot-instance-advisor:
-accessKeyId string
Your accessKeyId of cloud account
-accessKeySecret string
Your accessKeySecret of cloud account
-cutoff int
Discount of the spot instance prices (default 2)
-family string
The spot instance family you want (e.g. ecs.n1,ecs.n2)
-limit int
Limit of the spot instances (default 20)
-maxcpu int
Max cores of spot instances (default 32)
-maxmem int
Max memory of spot instances (default 64)
-mincpu int
Min cores of spot instances (default 1)
-minmem int
Min memory of spot instances (default 2)
-region string
The region of spot instances (default "cn-hangzhou")
-resolution int
The window of price history analysis (default 7)Run the following command to query the prices of instance types in the current region.
accessKeyId,accessKeySecret, andregionparameters are required. Set the parameters to the actual values.
./spot-instance-advisor --accessKeyId=<id> --accessKeySecret=<secret> --region=<cn-zhangjiakou>Set the ratio of spot instances to pay-as-you-go instances
Setting the ratio of spot instances to pay-as-you-go instances in a node pool allows you to reduce costs while maintaining sufficient pay-as-you-go instances for stability.
The cluster version must be later than 1.9. If you need to upgrade your cluster, see Update the Kubernetes version of an ACK cluster.
Make sure that you have a sufficient node quota in the cluster. For more information about node quotas and how to apply for a quota increase, see Limits.
When adding an existing node, ensure that the ECS instance in your VPC is associated with an elastic IP address (EIP) or a NAT gateway is configured for the VPC. The node must have internet access, otherwise it cannot be added.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster to manage and click its name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Node Pools page, click Create Node Pool and configure the node pool as prompted.
The following table describes only the key parameters. For more information, see Create and manage node pools.
Parameter
Description
VSwitch
We recommend that you select multiple vSwitches in different zones to ensure high availability.
Billing Method
Select spot Instance.
Expand the advanced options below and configure the following parameters.

Scaling Policy
Priority: The system scales the node pool based on the priorities of the vSwitches that you select for the node pool. The ones you select are displayed in descending order of priority. If Auto Scaling fails to create ECS instances in the zone of the vSwitch with the highest priority, Auto Scaling attempts to create ECS instances in the zone of the vSwitch with the next highest priority.
Cost Optimization: The system creates instances based on the vCPU unit prices in ascending order.
If the Billing Method of the node pool is set to Preemptible Instance, such instances are preferentially created. You can also set the Percentage of Pay-as-you-go Instances parameter. If preemptible instances cannot be created due to reasons such as insufficient stocks, pay-as-you-go instances are automatically created as a supplement.
Distribution Balancing: The even distribution policy takes effect only when you select multiple vSwitches. This policy ensures that ECS instances are evenly distributed among the zones (the vSwitches) of the scaling group. If they are unevenly distributed due to reasons such as insufficient stocks, you can perform a rebalancing operation.
Use Pay-as-you-go Instances When Spot Instances Are Insufficient
If you select this check box and preemptible instances cannot be created due to reasons such as price or inventory, ACK automatically attempts to create pay-as-you-go instances to meet your requirements for ECS instances.
Enable Supplemental Spot Instance
If you select this check box, ACK attempts to scale out new instances for compensation when it receives a system message that a preemptible instance is about to be reclaimed (5 minutes before the instance is reclaimed).
If the compensation is successful, ACK drains the old node and removes it from the cluster. If the compensation fails, ACK does not drain the old node. The active release of preemptible instances may cause service exceptions. After the compensation fails, ACK automatically purchases instances to maintain the expected number of nodes when the inventory is restored or the price condition is met. For more information, see Best practices for using preemptible instances in node pools.
To improve the success rate of compensation, we recommend that you also enable Supplement With Pay-as-you-go Instances.
After configuration is complete, you can click Actions in the node pool list and select Details. Then, click the Overview tab. In the Node Configurations section, you can view the percentage of pay-as-you-go instances.
Check whether a spot instance is about to expire
To avoid unexpected expiration and release of spot instances, ACK provides the ack-node-problem-detector (NPD) component to notify you when spot instances are about to be released.
To install the NPD component, see Step 1: Install the ack-node-problem-detector component.
In ACK clusters, ECS instances serve as nodes to host services. If you specify spot instance or subscription as the billing method when creating an ECS instance, the instance will be automatically released at expiration. Without advance pod eviction, node draining, or node replacement, services running on the instance may be interrupted. If a master node instance is released, cluster-level issues may occur. To prevent such problems, ACK uses the NPD component to monitor the InstanceExpired status and identify instances that are about to be released.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click the name of the one you want to change. In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Nodes page, find the node that you want to check and click the node name or choose in the Actions column.
On the node details page, check the status of the InstanceExpired condition.
In the Status section, check the status of the InstanceExpired condition.

The following table describes the states of InstanceExpired condition:
State of InstanceExpired
Description
True
If the InstanceExpired condition is in the True state and the Content is InstanceToBeTerminated, it indicates that the spot instance is about to expire and be released.
False
If the InstanceExpired condition is in the False state and the Content is InstanceNotToBeTerminated, it indicates that the spot instance is not about to expire.
Unknown
This state indicates that an error occurred on the plugin. submit a ticket for solutions.
If the InstanceExpired condition is in the True state, an event is generated in the Events section, as shown in the following figure.

If the InstanceExpired condition is in the True state, it indicates that the spot instance is about to expire and be released. To prevent interruption of applications running on this node, schedule them to other nodes. For more information, see Schedule application pods to the specified node.
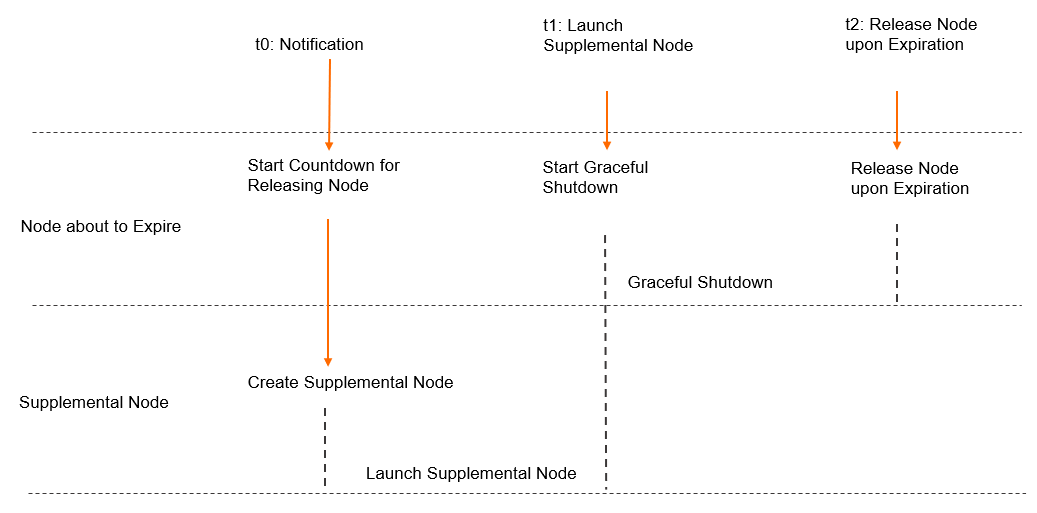
Graceful shutdown of spot instances
The graceful shutdown of spot instances includes monitoring and notification, supplementation of instances before reclamation, and custom operations on nodes to be released.
Monitoring and notification
ACK uses Node Problem Detector (NPD) to monitor the status of spot instances and sends notifications when they are about to expire.
If a spot instance is not about to expire, the value of InstanceExpired is False.

If a spot instance is about to expire, the value of InstanceExpired is True. In this case, ACK generates a cluster event to notify you that the spot instance is about to expire.

Enable Supplemental Preemptible Instances
When a spot instance expires and is released, services deployed on it are suspended. ACK provides methods to help you respond to this situation promptly. You can configure auto scaling, monitor instance status, and receive notifications when instances are about to expire. However, these methods are implemented after instances are reclaimed, and available resources don't increase until new instances are added. To address this issue, ACK can supplement spot instances before they're reclaimed, creating new instances before existing ones expire.
After enabling supplemental spot instances, ACK automatically checks for instances about to expire. When one is detected, ACK triggers a scale-out activity to add a new supplemental instance. After the supplemental instance starts running, the release process begins for the expiring instance. Its status is set to unschedulable, then it's drained and removed. This allows workloads to migrate smoothly to other nodes, avoiding service interruptions.
If supplementation fails due to reasons such as insufficient stock, ACK does not drain the old node. Active release of spot instances may cause service exceptions. After supplementation fails, when stock is restored or price conditions are met, ACK automatically purchases instances to maintain the expected node count.
To increase the success rate of supplementation, we recommend also enabling Enable Supplemental Pay-as-you-go Instances.
Supplementation does not interrupt the reclamation process. A spot instance will be reclaimed 5 minutes after notification, regardless of whether you enable Enable Supplemental Preemptible Instances.
Custom operations on nodes to be released
When gracefully shutting down a node, you might need to perform additional operations, such as removing node information from DNS records. To perform custom operations on nodes to be released, we recommend monitoring the InstanceExpired field in the node status or configuring a listener for InstanceToBeTerminated events. When you receive notification that a spot instance is about to expire or be released, you can perform a graceful shutdown and then execute your custom operations. For more information about checking instance expiration status, see Check whether a spot instance is about to expire.